Aerosol and aerosol-cloud interactions

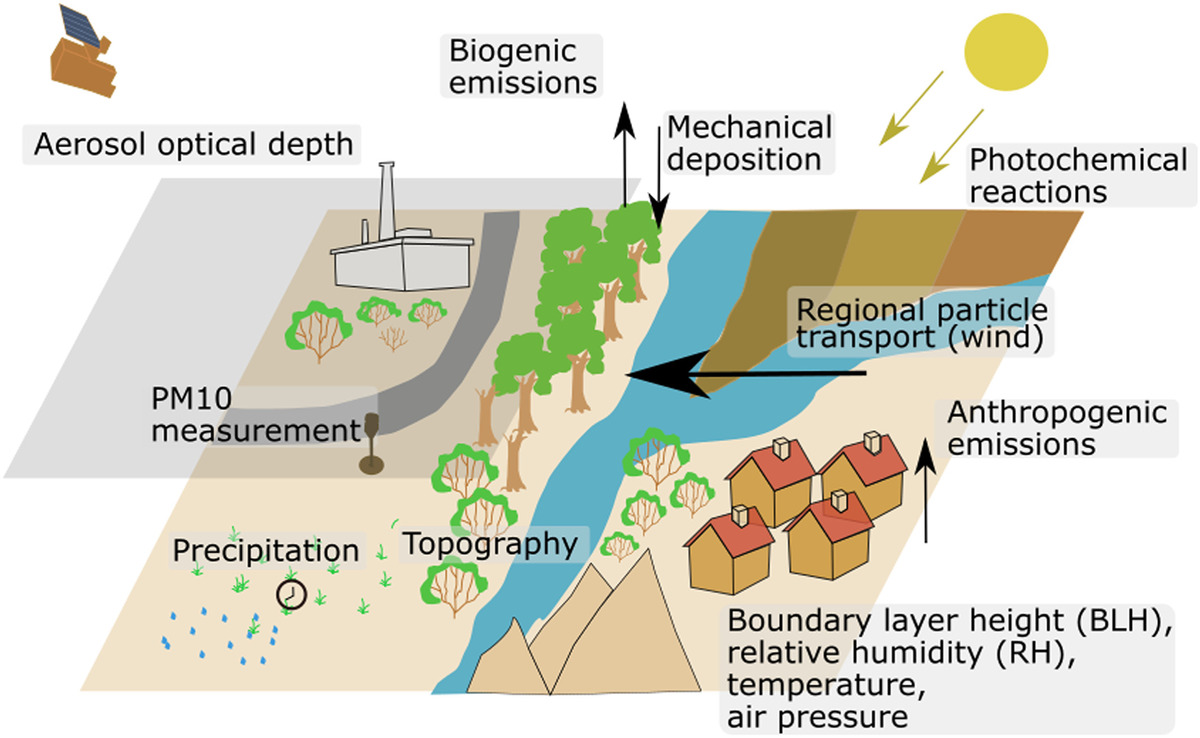
The interactions of aerosols, clouds and meteorological conditions impact the Earth’s radiation budget and are of great importance for the climate system. On a local scale, these interactions influence the heat island effect in urban areas. In addition, aerosols are a key factor for air quality and thus directly affect human well-being. However, the observation and modeling of individual processes is challenging as they are often complex, multicausal and occur on various temporal and spatial scales.
To improve the regional-scale estimation of air quality and to better understand processes of the aerosol-cloud-meteorology system on a global and local scale, we combine cloud and aerosol parameters from satellite images (SEVIRI; MODIS; MAIAC) with meteorological parameters (ERA-Interim, ERA5) as well as ground-based PM10 measurements. Therefore, we rely on various state of the art machine learning approaches. The analysis of isolated relationships, the models' ability to predict cloud properties and aerosol spatial distributions using meteorological information provides new insights into aerosol and cloud processes and shows new capabilites for the use of satellite data to estimate local air quality. RePAQ, GEOPAC
| Title | Contact | Funding | End Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regional Patterns of Air Quality (RePAQ) | Roland Stirnberg |
Graduate School for Climate and Environment (GRACE) |
2020 |
| A geographical perspective on aerosol-cloud interactions (GEOPAC) | Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) |
2017 |