CARIBIC H₂O Isotope Analyzer
The CARIBIC H₂O Isotope Analyzer (CHISA) is a high-precision infrared absorption spectrometer developed for on-site measurements of atmospheric water isotopes. As part of the IAGOS-CARIBIC project, CHISA employs Optical Feedback Cavity Enhanced Absorption Spectroscopy (OFCEAS), a technique (e.g., Morville et al., 2014) that achieves remarkable sensitivity for detecting isotopic variations in environments with water vapor concentrations as low as 5 ppm.
The instrument uses two spectrometers—one for water vapor and the other for total water, including ice crystals (Miltner, 2025). The high-finesse optical feedback cavity, where laser light is reflected thousands of times, results in an effective optical path length of >10 km. This design significantly enhances sensitivity, enabling the detection of subtle isotopic shifts in δ¹⁸O and δD. CHISA is scheduled for deployment in upcoming CARIBIC flights, advancing long-term atmospheric monitoring.
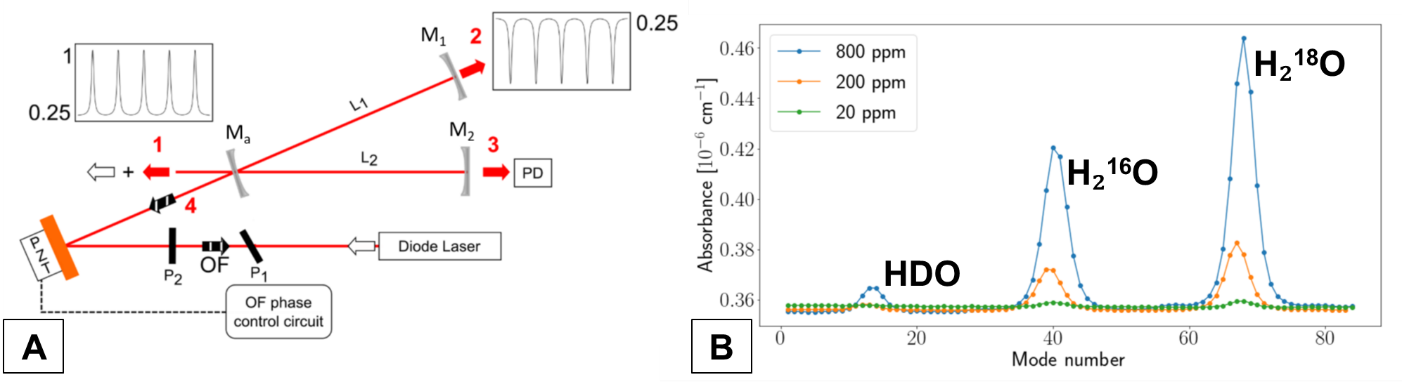
B: Absorption spectra recorded by CHISA for different water vapor mixing ratios and isotopologues, showing clear spectral separation (Miltner, 2025).
References
Morville, J., Romanini, D., and Kerstel, E. (2014). Cavity enhanced absorption
spectroscopy with optical feedback. Springer Series in Optical Sciences,179:163-209.
Miltner, M. (2025). Development of an aircraft-based isotope analyzer for water vapor using OFCEAS (Doctoral dissertation). Université Grenoble Alpes.
